Coordinates systems
Several coordinate systems are available for flexibly describing targets of procedures and locations.
Table of contents
- Anatomical Reference Points
- Stereotaxic Coordinate System Conventions
- Stereotaxic Bregma-Based Absolute Coordinates
- Stereotaxic Bregma-Based Surface Coordinates with Depth
- Stereotaxic Lambda-Based Absolute Coordinates
- Stereotaxic Lambda-Based Surface Coordinates with Depth
- Common Coordinate Framework XYZ Absolute Coordinates
- External XYZ Coordinates with Angles
- API access
Anatomical Reference Points
In neurosurgery or in research, it is important to define coordinates for where in the brain a surgical intervention will take place. These coordinates rely on anatomical markers that are uniform across individuals. There are two major anatomical markers on the dorsal surface of the brain that are formed when the plates of the skull fuse during development, and these markers are used to identify the location of various anatomical structures of the brain.
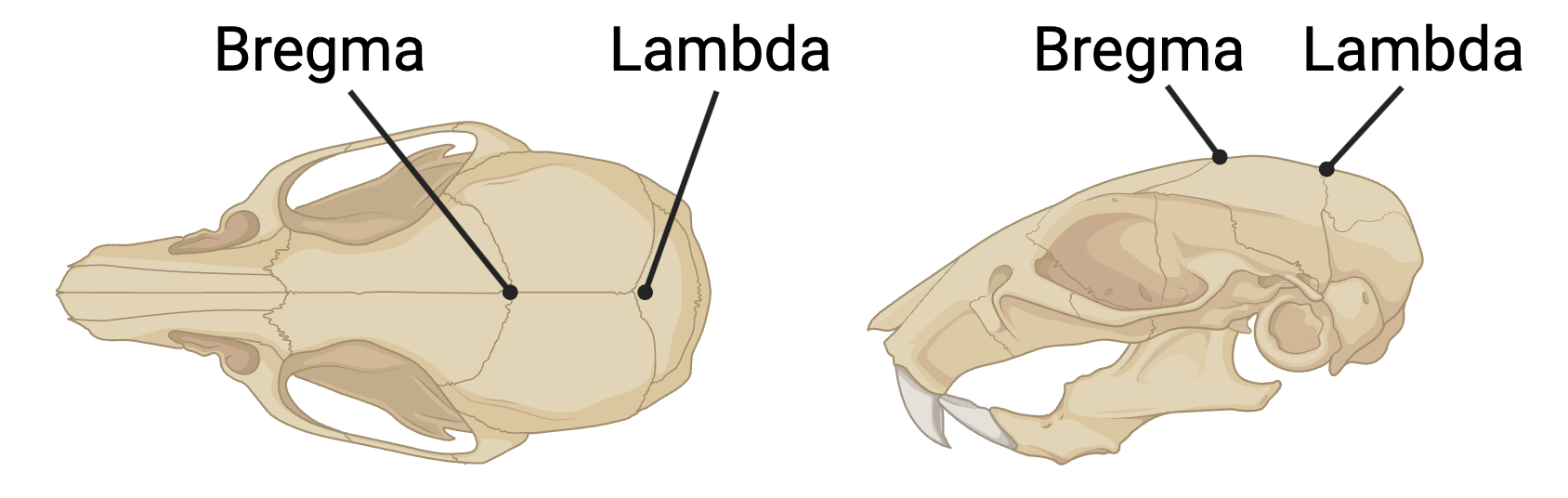
Bregma: the anatomical point on the skull at which the coronal suture (between frontal and parietal bones) is intersected perpendicularly by the sagittal suture (between left and right parietal bones).
Lambda: the meeting point of the sagittal suture (between left and right parietal bones) and the lambdoid suture (between parietal and occipital bones).
Both points serve as standard reference points for stereotaxic coordinates in neuroscience research.
Stereotaxic Coordinate System Conventions
Basic Coordinate System
All stereotaxic coordinate systems in BrainSTEM follow a right-handed coordinate system with the following conventions:
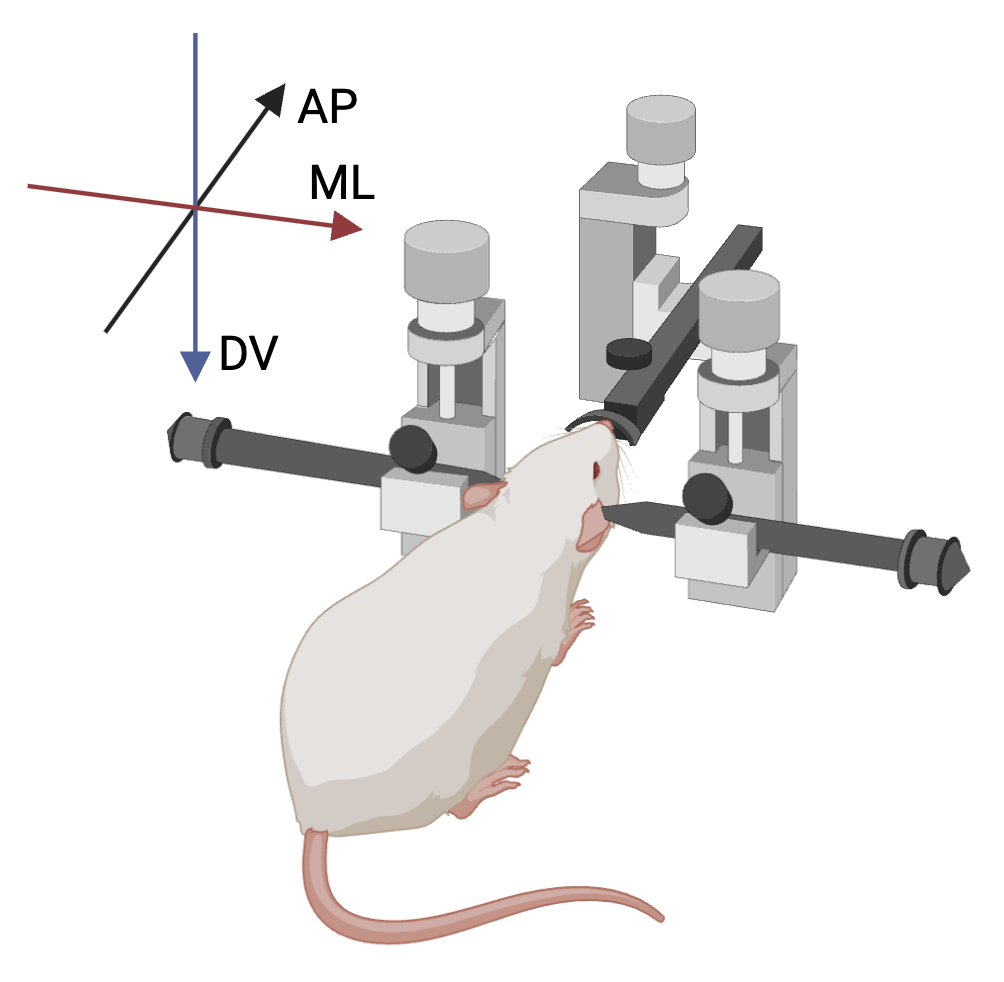
- AP (Anterior-Posterior) axis:
- Primary reference axis
- Positive values are anterior to reference point
- ML (Medial-Lateral) axis:
- Following right-hand rule relative to AP axis
- Positive values are to the right (as seen from behind)
- DV (Dorsal-Ventral) axis:
- Following right-hand rule
- Positive values are ventral
Angle Measurement System
By default, angles are defined by three rotations: 1. The AP angle, rotating clockwise around ML 2. The ML angle, rotating clockwise around AP 3. The rotation angle, rotating clockwise around the object’s depth axis
Proper understanding and application of these angles is critical for accurate probe placement and experimental reproducibility.
All stereotaxic measurements use three angles to specify orientation:
AP angle (Anterior-Posterior rotation):
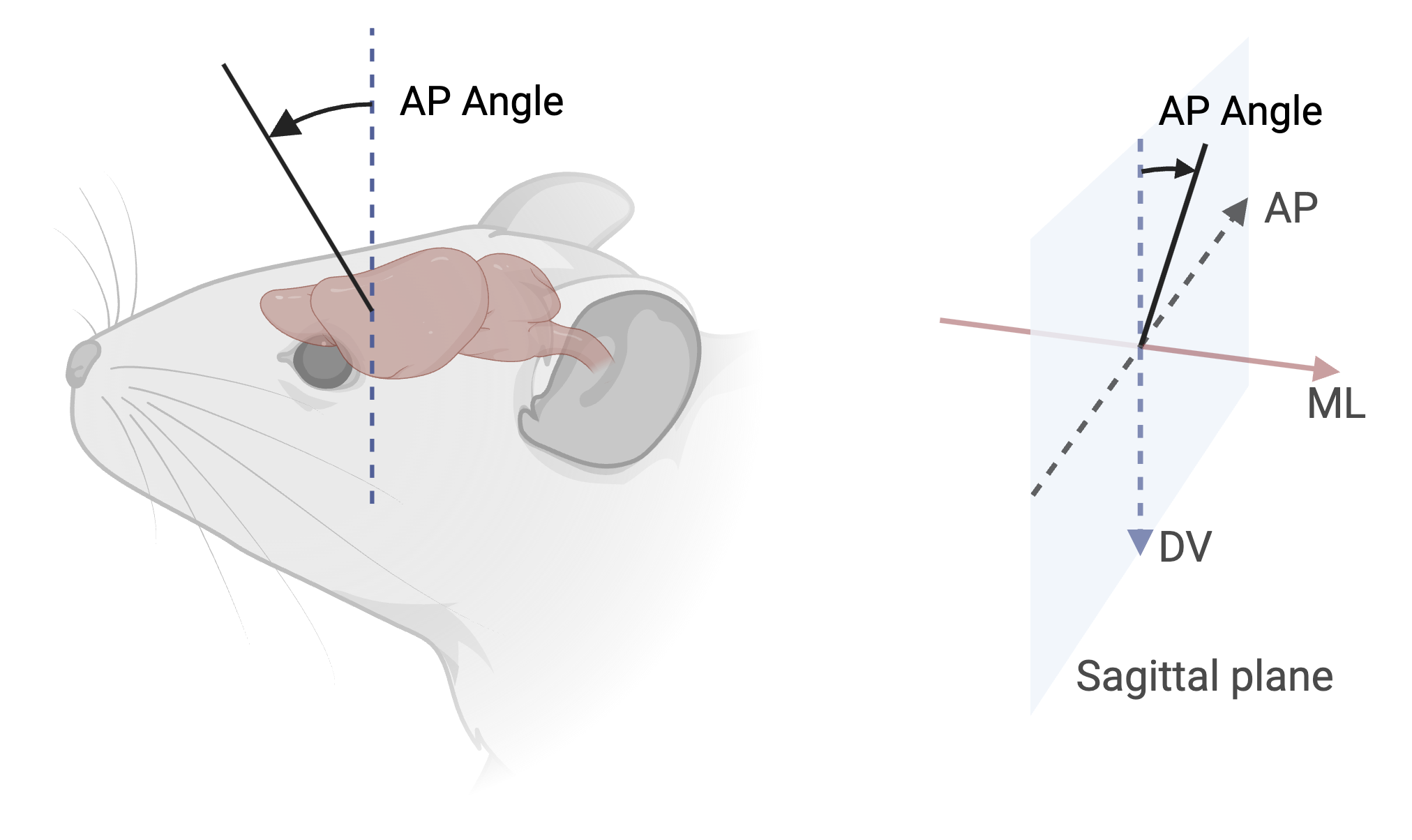
- Measured as rotation from the vertical axis in the sagittal plane
- 0° represents vertical along DV axis
- Range: -180° to +180°
- Positive values indicate anterior rotation
- Example: +15° indicates probe tiltet 15° anteriorly from vertical
ML angle (Medial-Lateral rotation):
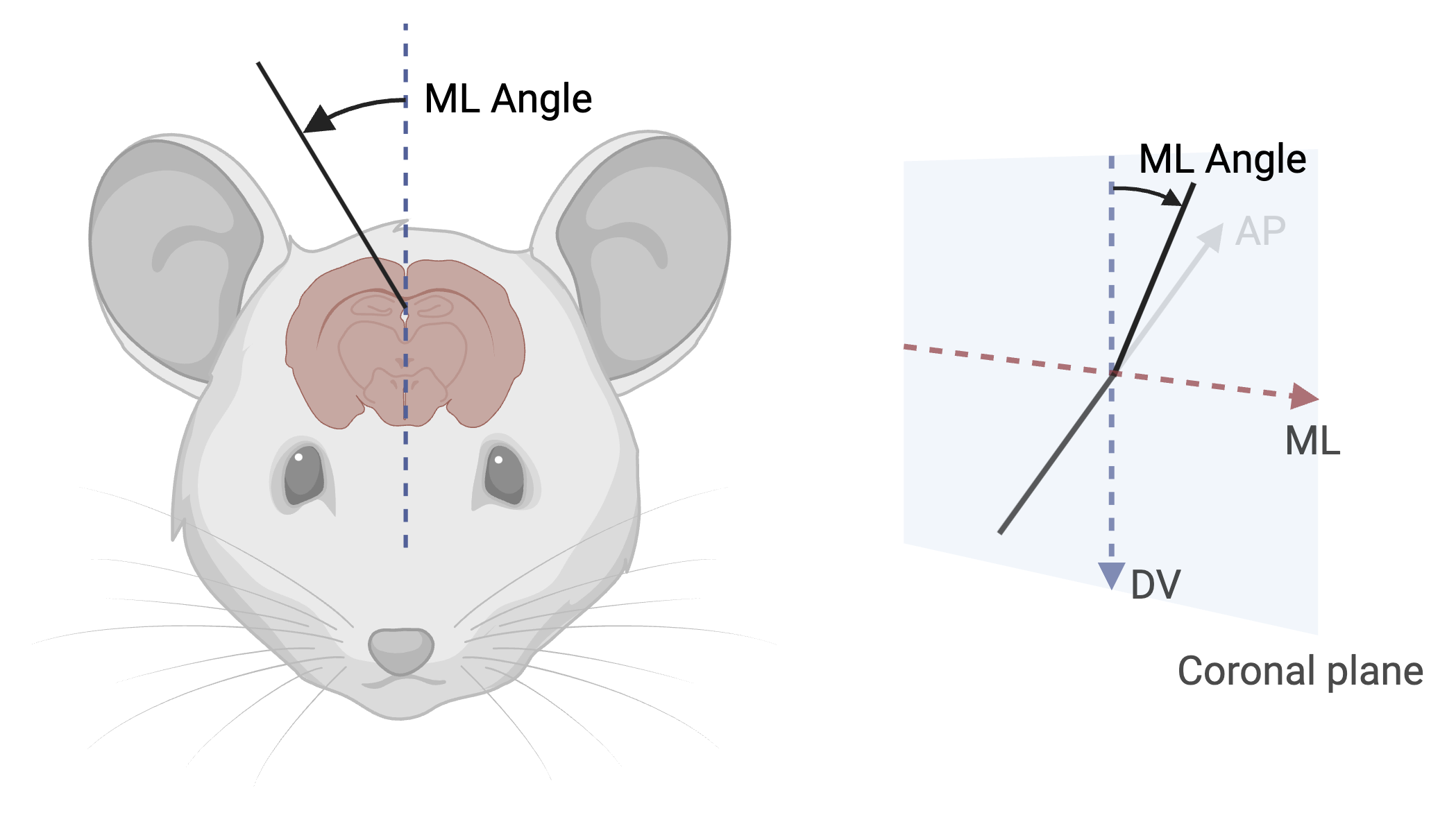
- Measured as rotation from the vertical axis in the coronal plane
- 0° represents vertical along DV axis
- Range: -180° to +180°
- Positive values indicate rightward/clockwise rotation (as seen from behind)
- Example: +20° indicates probe tiltet 20° to the right from vertical
Rotation angle (around probe axis):
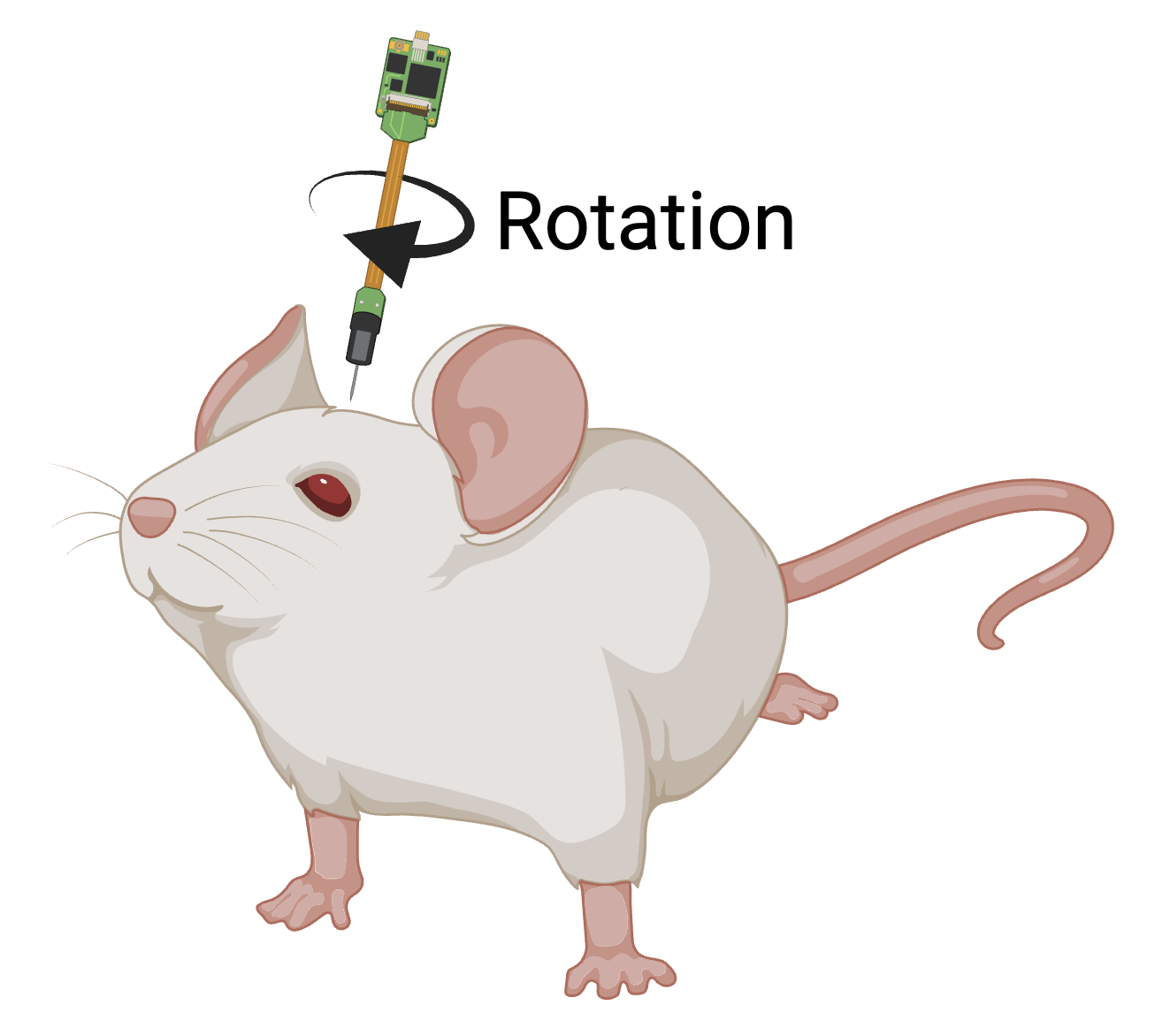
- 0° when probe features align with the coronal plane
- Range: -180° to +180° (or 0° to 360°)
- Positive rotation is clockwise when viewed from above
Stereotaxic Bregma-Based Absolute Coordinates
Uses Bregma as reference point in stereotaxic right-hand coordinate system:
- AP axis: Anterior positive, posterior negative
- ML axis: Right positive, left negative
- DV axis: Ventral positive, dorsal negative
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
AP coordinate (mm) | Anterior-Posterior coordinate from Bregma (float) |
ML coordinate (mm) | Medial-Lateral coordinate from Bregma (float) |
DV coordinate (mm) | Dorsal-Ventral coordinate from Bregma (float) |
AP angle (degrees) | AP angle in sagittal plane (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
ML angle (degrees) | ML angle in coronal plane (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
Rotation (degrees) | Rotation around probe axis (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
Stereotaxic Bregma-Based Surface Coordinates with Depth
Uses Bregma reference with depth from surface instead of DV coordinates. Same AP and ML axes as Bregma-Based Absolute.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
AP coordinate (mm) | Anterior-Posterior coordinate from Bregma (float) |
ML coordinate (mm) | Medial-Lateral coordinate from Bregma (float) |
Depth (mm) | Depth from brain surface (float) |
AP angle (degrees) | AP angle in sagittal plane (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
ML angle (degrees) | ML angle in coronal plane (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
Rotation (degrees) | Rotation around probe axis (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
Stereotaxic Lambda-Based Absolute Coordinates
Uses Lambda as reference point with same coordinate system conventions as Bregma-Based Absolute.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
AP coordinate (mm) | Anterior-Posterior coordinate from Lambda (float) |
ML coordinate (mm) | Medial-Lateral coordinate from Lambda (float) |
DV coordinate (mm) | Dorsal-Ventral coordinate from Lambda (float) |
AP angle (degrees) | AP angle in sagittal plane (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
ML angle (degrees) | ML angle in coronal plane (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
Rotation (degrees) | Rotation around probe axis (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
Stereotaxic Lambda-Based Surface Coordinates with Depth
Uses Lambda reference with depth from surface. Same AP and ML axes as Lambda-Based Absolute.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
AP coordinate (mm) | Anterior-Posterior coordinate from Lambda (float) |
ML coordinate (mm) | Medial-Lateral coordinate from Lambda (float) |
Depth (mm) | Depth from brain surface at Lambda (float) |
AP angle (degrees) | AP angle in sagittal plane (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
ML angle (degrees) | ML angle in coronal plane (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
Rotation (degrees) | Rotation around probe axis (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
Common Coordinate Framework XYZ Absolute Coordinates
The Common Coordinate Framework (CCF) is defined in a basic image coordinate system, using the top-left-front pixel as its origin, and incrementing in the X, Y and Z axes up to the number of pixels in each dimension (AP, DV, ML respectively). Superior-Inferior (SI) is used instead of DV in below figure, and Left-Right (LR) instead of ML. It was not designed as a targeting coordinate system. Using some transformations the CCF can be roughly aligned to the stereotaxic atlas, however, since it was not it’s intended purpose one should take caution when using the CCF for targeting, even after applying these transformations.
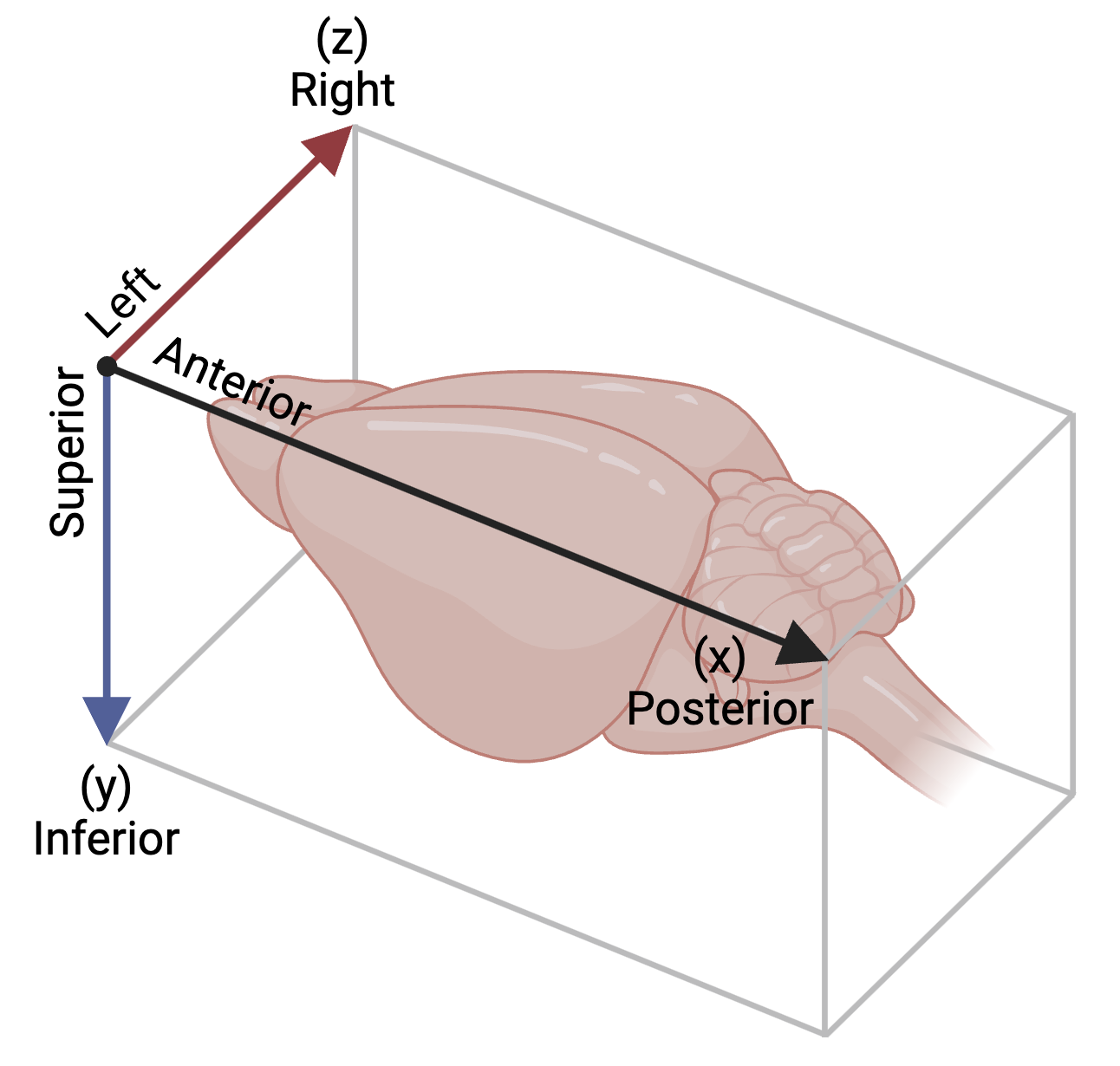
CCF can be mapped to the stereotaxic axes:
- X = AP axis (posterior positive)
- Y = DV or SI axis (ventral/inferior positive)
- Z = ML axis (right positive)
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
X coordinate (mm) | Position along AP axis (float) |
Y coordinate (mm) | Position along DV axis (float) |
Z coordinate (mm) | Position along ML axis (float) |
X angle (degrees) | X/AP angle in sagittal plane (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
Z angle (degrees) | Z/ ML angle in coronal plane (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
Rotation (degrees) | Rotation around probe axis (float; range: -180° to +180°) |
External XYZ Coordinates with Angles
This system provides an absolute reference frame independent of anatomical landmarks.
A three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system using absolute positions relative to an external reference point.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
X coordinate (m) | Absolute X coordinate in meters, horizontal positioning in local reference frame (float) |
Y coordinate (m) | Absolute Y coordinate in meters, vertical positioning in local reference frame (float) |
Z coordinate (m) | Absolute Z coordinate in meters, height in local reference frame (float) |
X angle (degrees) | Rotational angle around X axis (float; range: -180° to 360°) |
Y angle (degrees) | Rotational angle around Y axis (float; range: -180° to 360°) |
Z angle (degrees) | Rotational angle around Z axis (float; range: -180° to 360°) |
API access
The API allows for programmable access to Coordinates, enabling you to read, edit, and delete coordinates through the API. Learn more about the coordinates’ fields and data structure on the Coordinates API page.